Contact & Frequently Asked Questions
Address
Unit 1 /8 Weld Street
Prestons, NSW 2170 Australia
Phone Number
+61 (02) 8783 6633
Email Address
Thanks for your message! We’ll be in touch soon.
Frequently Asked Questions
A: The full name of UPS is “Uninterruptible Power Supply”. It will immediately supply computers mains to maintain the normal operation when power failure or abnormity.
A: Un-stable power quality will effect the operation of computers. UPS will not only immediately supply power to computers while power failure, but also protect against wide utility voltage. It will also offer users pure power and store your important data whether you are there or not. Therefore, UPS becomes more and more important equipment for computer & 3C users.
A: There are three typical types of UPS: OFF-LINE, ON-LINE, and LINE INTERACTIVE.
A: Off-line UPS will supply power only when power failure.
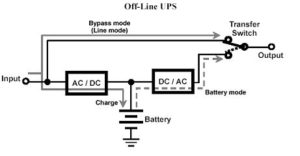
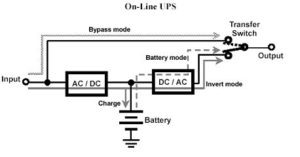
A: Under normal situation, On-line UPS will supply power after rectification and will transfer to bypass only when UPS is out of order, overload, or overheat. Normally, the On-line UPS provides the pure Sinewave output which is same as the mains provide by power plants.
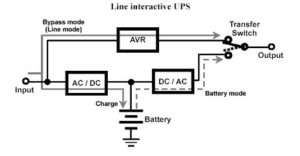
A: Under normal situation, Line Interactive UPS will supply power from bypass through transformer. At this moment, transformer becomes charger. When power failure, transformer will transfer battery power to AC output.
- Understand specifications of all UPS.
- Consider the requirements of power quality.
- Understand the current capacity of UPS and consider the future expanding.
- Choose the reputed brands and manufacturers.
- Choose UPS based on your requirements.
- UPS reliability and stability.
- The excellent engineers and the ability of products creation.
- High efficiency and low noise.
- Suppliers’ reputation and financial situation.
- International safety approvals such as TUV, UL, CSA, and so on.
- Plant certifications such as ISO9001, ISO9002, and so on.
A: In fact, power failure is one of power problem. The other power problems such as high voltage, low voltage, and spike are the main problems. The purposes of UPS is to provide customers the overall power protection such as voltage regulation, surge protection, spike, and sags protection. It also provides extended back up time without any limitation.
A: RJ11 connector is used to protect the phone line. Hence, you can connect your phone; fax machine, modem and ADSL with it for better protection.
A: Except the blackout, there are Sags, Spikes, Surges, Noise & Transients will make the PC or other high technical equipment damage or shorten the lifetime.
- Blackout, power slump, power surge,
- Continuous under voltage, continuous over voltage,
- Frequency fluctuation, interference of computers,
- Switching transient, harmonic distortion, etc.
An UPS can perform
- Power down protection
- Under-voltage and over-voltage protection
- Waveform distortion correction
- Frequency stabilization
- Voltage regulation
- Normal mode noise rejection
- Common mode noise rejection
- Surge protection
- Transient response protection
- Power supply monitoring
A UPS has internal batteries to guarantee that continuous power is provided to the equipment even if the power supply stops providing power.
Advantages:
- Computer jobs don't stop in case of the power failure.
- Users do not inconvenienced when computer is out of power.
- Equipment does not incur the stress of another (hard) power cycle.
- Data isn't lost because a machine shut down without doing a "sync" or equivalent to flush cached or real time data.
It depends on how big a UPS do you have and what kind of equipment it protects? For most typical computer workstations, one might have a UPS that was rated to keep the machine alive through a 15 minute power loss. If you need a machine to survive hours without power, you should probably look at a more robust power backup solution. Even if a UPS has a very small load, it must still operate it's DC (battery) to AC converter, which costs power.
Typically, a UPS has a VA rating. The VA rating is the maximum number of Volts * Amps it can deliver. The VA rating is not the same as the power drain (in Watts) of the equipment. Computers are notoriously non-resistive. A typical PF (power factor: Watts/VA) for workstations may be as low as 0.6, which means that if you record a drain of 100 Watts, you need a UPS with a VA rating of 167. Some literature suggests that 0.7 may be a good conversion factor, but this will depend heavily on the machine.
- The main specs for hardware are:
- Operation model: offline, line interactive, online
- Input voltage range
- Input frequency range
- Input power factor
- Load power factor
- Over load capacity
- Transfer time
- The stability of output voltage
- The distortion of output voltage
- Crest ratio
- Ability of taking 100% unbalanced load
- Cold start function
- Bypass function
- Compatible with generators
- Battery management level
- UPS efficiency
| The problems of utility lines | back up UPS | line interactive UPS | online UPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power surges | No solution | limited solution | complete solution |
| High voltage spikes | No solution | limited solution | complete solution |
| Waveform slump | limited solution | limited solution | complete solution |
| Electronic interference | limited solution | limited solution | complete solution |
| Frequency fluctuation | no solution | no solution | Track and lock phase within certain range |
| Continuous high voltage or low voltage | limited solution | limited solution | complete solution |
| High voltage transient | no solution | limited solution | complete solution |
| Power down | complete solution | complete solution | complete solution |
